研究项目和附属机构
研究兴趣
Radiation damage to bone and progenitor cells; mechanical regulation of bone cell behavior; osteoclast lineage cells; orthopedic tissue engineering.
EDUCATION
研究抽象
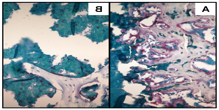 Cellular Mechanisms Mediating Therapeutic Radiation Damage to Bone: A common complication following focal radiation therapy for soft tissue sarcoma is late-onset insufficiency fracture of the bone. While radiation-induced morphological changes to the bone have been documented, these changes alone do not explain the increased risk for fragility fracture. 采用小鼠后肢局灶性辐照模型, 我们已经记录了一个早期的, transient increase in osteoclast numbers followed by persistent loss of osteoclasts long-term, 以及辐照后骨基质的大量改变. These alterations in osteoclast number correlate temporally with loss of trabecular bone. Persistence of poor quality bone matrix post-irradiation highlights the importance of retaining functional osteoclast and osteoclast progenitor cell populations long-term. We are characterizing this radiation-induced progenitor cell damage and osteoclast dysfunction, and investigating potential preventative pharmacologic interventions. (资助:鲍德温基金会)
Cellular Mechanisms Mediating Therapeutic Radiation Damage to Bone: A common complication following focal radiation therapy for soft tissue sarcoma is late-onset insufficiency fracture of the bone. While radiation-induced morphological changes to the bone have been documented, these changes alone do not explain the increased risk for fragility fracture. 采用小鼠后肢局灶性辐照模型, 我们已经记录了一个早期的, transient increase in osteoclast numbers followed by persistent loss of osteoclasts long-term, 以及辐照后骨基质的大量改变. These alterations in osteoclast number correlate temporally with loss of trabecular bone. Persistence of poor quality bone matrix post-irradiation highlights the importance of retaining functional osteoclast and osteoclast progenitor cell populations long-term. We are characterizing this radiation-induced progenitor cell damage and osteoclast dysfunction, and investigating potential preventative pharmacologic interventions. (资助:鲍德温基金会)
 Biochemical and Mechanical Alterations to Bone Following Radiotherapy: Radiation-induced bone fragility is best explained using a model that assumes embrittlement of bone's material properties following radiation. We hypothesize that this embrittlement may occur through biochemical alterations to the organic matrix and alterations to mineral crystallinity. 利用拉曼光谱, 机械测试, 晚期糖基化终产物积累的评估, we are exploring time and location-dependent biochemical alterations to bone following radiation therapy. (Funding: NIH/NIAMS, PI: Timothy Damron, Co-Is: Kenneth Mann, David Kohn & 迈克尔·莫里斯(密歇根大学)
Biochemical and Mechanical Alterations to Bone Following Radiotherapy: Radiation-induced bone fragility is best explained using a model that assumes embrittlement of bone's material properties following radiation. We hypothesize that this embrittlement may occur through biochemical alterations to the organic matrix and alterations to mineral crystallinity. 利用拉曼光谱, 机械测试, 晚期糖基化终产物积累的评估, we are exploring time and location-dependent biochemical alterations to bone following radiation therapy. (Funding: NIH/NIAMS, PI: Timothy Damron, Co-Is: Kenneth Mann, David Kohn & 迈克尔·莫里斯(密歇根大学)
 Novel Biomaterials for Stabilization and Repair of Critically Sized Bone Defects: We are investigating the use of novel shape-memory polymer scaffolds and electrospun shape-memory polymer sleeves as methods of rapidly stabilizing bone defects, 粉碎性骨折重建, and delivering antimicrobial and osteoinductive agents to facilitate autologous repair long-term. We have completed preliminary testing of this technology in a mouse femoral defect model, and are scaling up to larger animal models for eventual human application. (Funding: Nappi Family Awards, co-PI: James Henderson, Syracuse University)
Novel Biomaterials for Stabilization and Repair of Critically Sized Bone Defects: We are investigating the use of novel shape-memory polymer scaffolds and electrospun shape-memory polymer sleeves as methods of rapidly stabilizing bone defects, 粉碎性骨折重建, and delivering antimicrobial and osteoinductive agents to facilitate autologous repair long-term. We have completed preliminary testing of this technology in a mouse femoral defect model, and are scaling up to larger animal models for eventual human application. (Funding: Nappi Family Awards, co-PI: James Henderson, Syracuse University)
Publications:
1. Oest ME, Mann KA, Zimmerman ND, Damron TA. (2016) PTH(1-34) transiently protects against radiation-induced bone damage. 钙化组织国际在印刷前出版.
2. Baker RM,曾丽芳,Iannolo MT, Oest ME, Henderson JH. (2016) Self-deploying shape memory polymer scaffolds for grafting and stabilizing complex bone defects: a mouse femoral segmental defect study. 生物材料76:388 - 398.
3. Oest ME,李建军,李建军,李建军,李建军. (2015) Long-term loss of osteoclasts and unopposed cortical mineral apposition following limited field irradiation. 骨科杂志,33(3):334-342.
4. Oest ME, Damron TA. (2014) Focal therapeutic irradiation induces an early transient increase in bone glycation. 放射学研究,2004,18 (4):439- 443.
5. Oest ME,米勒马,霍华德基,曼卡. (2014) A novel in vitro loading system to produce supraphysiologic fluid shear stress. 生物力学学报,47(2):518-525.
6. Gong B, Oest ME, Mann KA, Damron TA, Morris MD. (2013) Raman Spectroscopy Demonstrates Prolonged Alteration of Bone Chemical Composition Following Extremity Localized Irradiation. 骨57 (1):252 - 258.
7. Keenawinna L, Oest ME, Mann KA, Spadaro JA, Damron TA. (2013) Zoledronic Acid Prevents Loss of Trabecular Bone Following Focal Irradiation in Mice. 放射学学报,2001,19 (1):89-99.
8. Wojtowitcz AM, Shekaran A, Oest ME, Dupont KM, Templeman KL, Hutmacher DW, Guldberg RE, Garcia AJ. (2010) Coating of biomaterial scaffolds with the collagen-mimetic peptide GFOGER for bone defect repair. 生物材料学报,31(9):2574-2582.
9. Liang C, Oest ME, Jones JC, Prater MR. (2009) Gestational high saturated fat diet alters C57BL/6 mouse perinatal skeletal formation. Birth Defects Research Part B Developmental and Reproductive Toxicology, 86(5):377-384.
10.Liang C, Oest ME, Prater MR. (2009) Intrauterine exposure to high saturated fat diet elevates risk of adult-onset chronic diseases in C57Bl/6 mice. Birth Defects Research Part B Developmental and Reproductive Toxicology, 86(5):362-369.
11.Oest ME, Jones JC, Hatfield C, Prater MR. (2008) Micro-CT evaluation of murine fetal skeletal development yields greater morphometric precision over traditional clear-staining methods. Birth Defects Research Part B Developmental and Reproductive Toxicology 83(6):582-589.
12.gudberg RE, Duvall CL, Peister A, Oest ME, Lin AS, Palmer AW, Levenston ME. (2008)多孔生物材料组织整合的三维成像. 生物材料学报,29 (28):3757-3761.
13.Guldberg RE, Oest ME,杜朋K, Peister A, Deutsch E, Kolambkar Y, Mooney D. (2007)生物增强聚合物支架用于骨修复. 中国生物医学工程学报[j] . 7(4):333-334.
14.Duty AO, Oest ME, Guldberg RE. (2007) Cyclic mechanical compression in vivo increases mineralization of cell-seeded polymeric orthopaedic tissue constructs. 生物力学学报,29(4):531-539.
15.Oest ME,杜邦KM,孔海杰,穆尼,DJ,古尔伯格RE. (2007) Quantitative assessment of scaffold and growth factor-mediated repair of critically sized bone defects. 骨科杂志,25(7):941-950.
16.Rai B, Oest ME,杜朋KM,何洪,赵淑华,郭德柏. (2007) Combination of platelet-rich plasma with polycaprolactone-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds for segmental bone defect repair. 生物医学工程学报,2011,(4):888-899.
17.Guldberg RE, Oest ME, Lin AS, Ito H, Chao X, Gromov K, Goater JJ, Koefoed M, Schwarz EM, O'Keefe RJ, Zhang X. (2004) Functional integration of tissue-engineered bone constructs. Journal of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions 4(4):399-400.
18. Guldberg RE, Ballock RT, Boyan BD, Duvall CL, Lin AS, Nagaraja S, Oest ME,刘建军,刘建军,刘建军. (2003) Analyzing bone, blood vessels, and biomaterials with microcomputed tomography. 医学与生物工程,22(5):77-83.
19. Bower CK, Parker JE, Higgins AZ, Oest ME, Wilson JT, Valentine BA, Bothwell MK, McGuire J. (2002) Protein antimicrobial barriers to bacterial adhesion: in vitro and in vivo evaluation of nisin-treated implantable materials. 胶体与表面[j] .生物工程学报,25(1):81-90.

